Did You know the Connection Between Oxygen Sensors and Fuel Efficiency
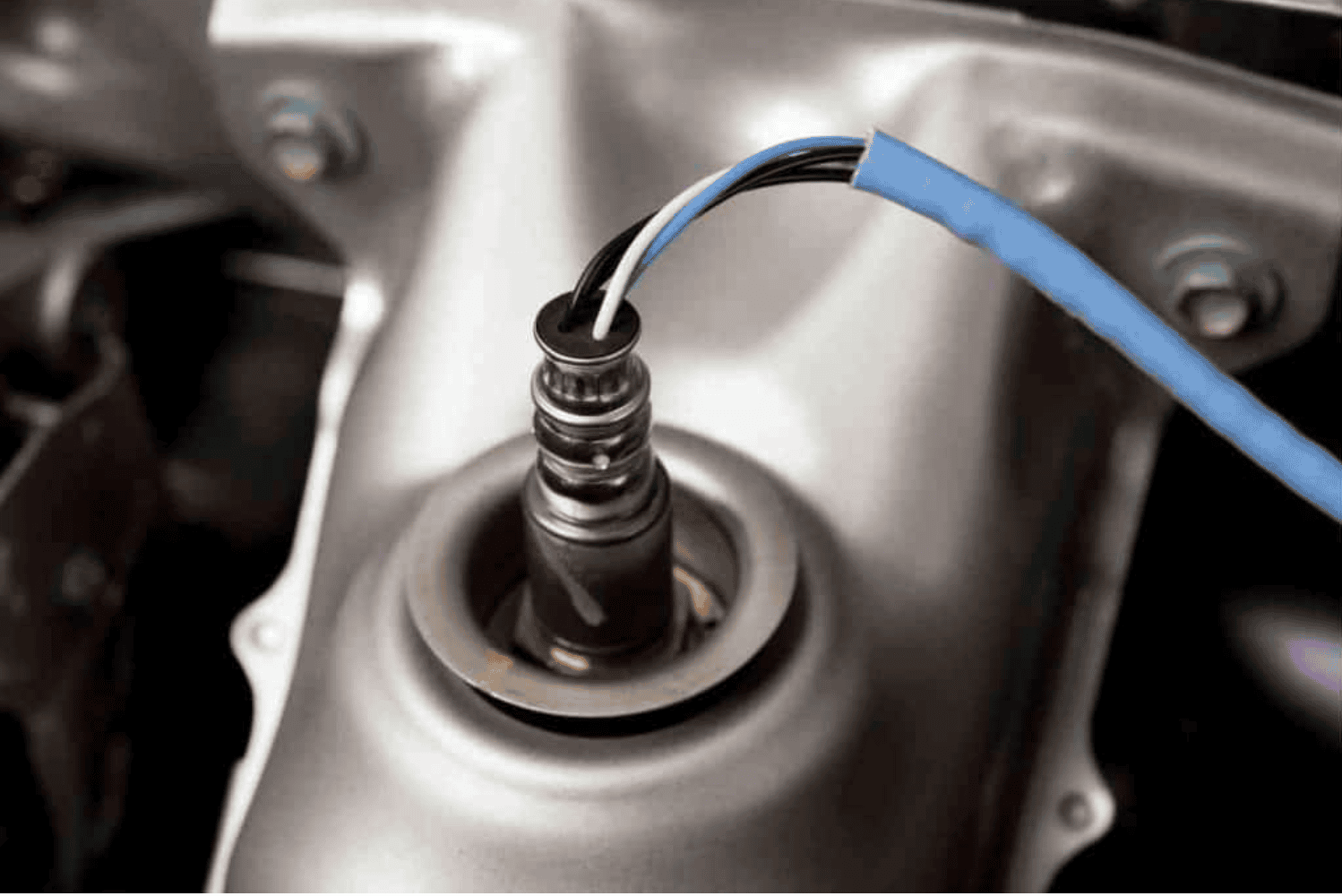

When discussing your vehicle's fuel economy, the Oxygen Sensor (O2 Sensor) is a crucial component we cannot ignore. Simply put, it acts like the "eyes" of your vehicle's engine, constantly checking if fuel combustion is happening correctly.
Let's understand this connection simply.
What Does the Oxygen Sensor Do?
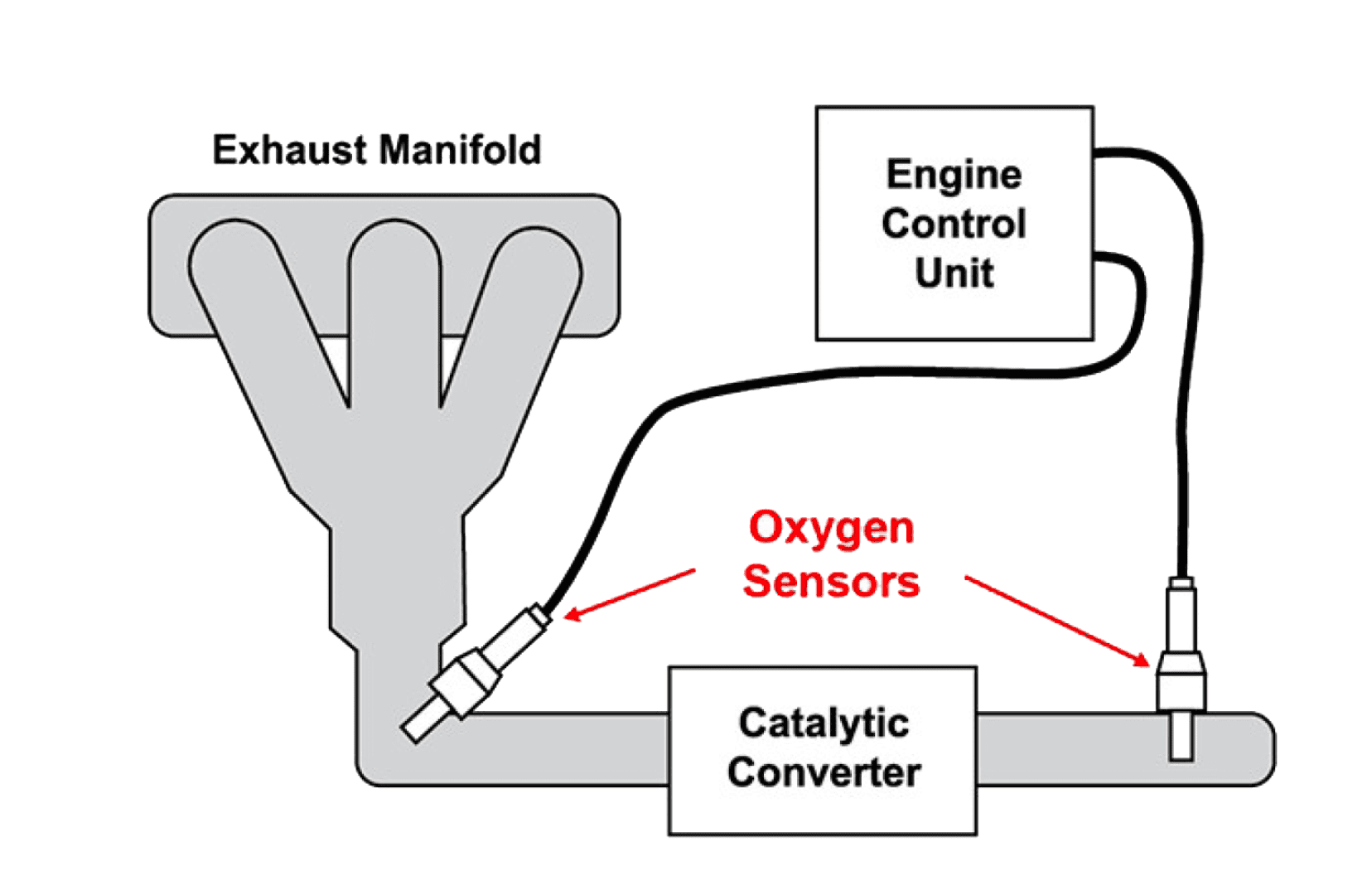
Generally, inside an engine, fuel and air mix in a specific ratio and burn. This sensor measures the amount of oxygen remaining in the exhaust fumes emitted by the engine. When this data is provided to the Engine Control Unit (ECU), the ECU decides the amount of fuel to send to the engine for the next cycle.
How Does It Affect Fuel Efficiency?
When the oxygen sensor doesn't work properly, the air and fuel ratio received by the engine gets disrupted. Often, due to the sensor providing incorrect data, the ECU releases more fuel than necessary (Rich Mixture) into the cylinders. This is why the vehicle's fuel consumption increases suddenly.
When the sensor malfunctions, the engine burns fuel unnecessarily. Excess fuel burning can cause black smoke emissions and difficulties in starting the engine.
How to Identify if the Sensor is Faulty?
This one small sensor can reduce your vehicle's fuel efficiency by 10% - 40%. The primary signs include the Check Engine Light illuminating on the dashboard, hearing unusual noises from the engine, or smelling fuel. It is very important to clean or replace this sensor, especially in vehicles driven between 80,000 - 100,000 km.
Also, a correctly functioning oxygen sensor can significantly reduce your fuel costs and minimize harmful emissions released into the environment. If your vehicle's fuel consumption has increased suddenly, the first place you should check is this Oxygen Sensor.
If your vehicle's Check Engine Light is on, ignoring it can cause significant loss to both the engine and your wallet in the future. Especially if this light is on due to an Oxygen Sensor fault, it is important to follow the steps below:
1. First Thing to Do is Scanning

Take the vehicle to a garage or service center and perform a computer diagnosis using an OBD-II Scanner. Through the resulting "Error Code" (for example: P0130, P0135), you can know exactly whether the problem is with the oxygen sensor itself or another wire connection.
2. Cleaning the Sensor
Sometimes the sensor is not broken, but provides incorrect data due to carbon buildup on it. In such cases, using a specialized Sensor Cleaner to clean it can save a lot of money.
3. Checking for Air Leaks
If there are holes in the pipes entering the engine (Intake Manifold) or exhaust pipes, the oxygen sensor thinks there is too much air in the engine. Then it provides excess fuel unnecessarily. Therefore, checking for leaks in pipes is very important.
4. Replacing the Sensor
If the sensor is completely dysfunctional, it has to be replaced with a new one. Rather than installing low-quality sensors, installing a sensor suitable for your vehicle (Genuine/OEM) allows you to maximize fuel economy.
Remember: Driving for a long time with the Check Engine Light on can disable your vehicle's Catalytic Converter (fume purification unit). Replacing it is about ten times more expensive than an oxygen sensor.