Different Types of Engines Explained

The engine is often called the heart of a vehicle. Its primary role is to convert thermal energy into mechanical energy, powering the vehicle and keeping it moving. Over the years, various types of engines have been developed to suit different vehicles and performance needs. Today, MotorGuide explores the main engine classifications used in the automotive industry.
How Are Engines Classified?
Engines can be classified in several ways based on:
- Place where the fuel is burned
- Design
- Number of strokes
- Type of fuel used
- Ignition method
- Number of cylinders
- Cylinder arrangement
1. According to the Place Where Fuel is Burned
- Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) – Fuel burns inside the engine. The most common is the four-stroke engine, which includes suction, compression, power, and exhaust strokes.
- External Combustion Engine – Fuel burns outside the engine, producing steam or heat pressure to generate power. Solid fuels can also be used in this system.
2. Based on the Design
- Reciprocating Engine – Built with pistons and cylinders, widely used in cars and motorcycles.
- Rotary (Wankel) Engine – Introduced in 1957, it features a triangular rotor inside an elliptical chamber, offering smooth performance in a compact design.
3. Based on the Number of Strokes
- Four-Stroke Engine – Requires four piston movements (suction, compression, power, exhaust) to complete one combustion cycle.
- Two-Stroke Engine – Completes one combustion cycle with just two piston strokes, often used in smaller motorcycles.
4. Based on the Fuel Used
- Petrol Engine – Runs on petrol fuel.
- Diesel Engine – Uses diesel fuel, known for higher torque and fuel efficiency.
- Gas Engine – Runs on LPG or CNG fuel, often more eco-friendly.
- Electric Engine – Powered entirely by electricity, becoming increasingly popular in modern EVs.
5. Based on the Ignition Method
- Compression-Ignition Engine – Air is compressed until it reaches a high temperature, igniting the fuel without a spark plug. Common in diesel engines.
- Spark-Ignition Engine – Uses a spark plug to ignite the fuel-air mixture, standard in petrol engines.
6. Based on the Number of Cylinders
- Single-Cylinder Engine – Contains only one cylinder, often seen in small motorcycles.
- Multi-Cylinder Engine – Includes two or more cylinders, delivering more power and smoother performance.
7. Based on Cylinder Arrangement
- In-line Engine – Cylinders are arranged in a straight line (2 to 8 cylinders).
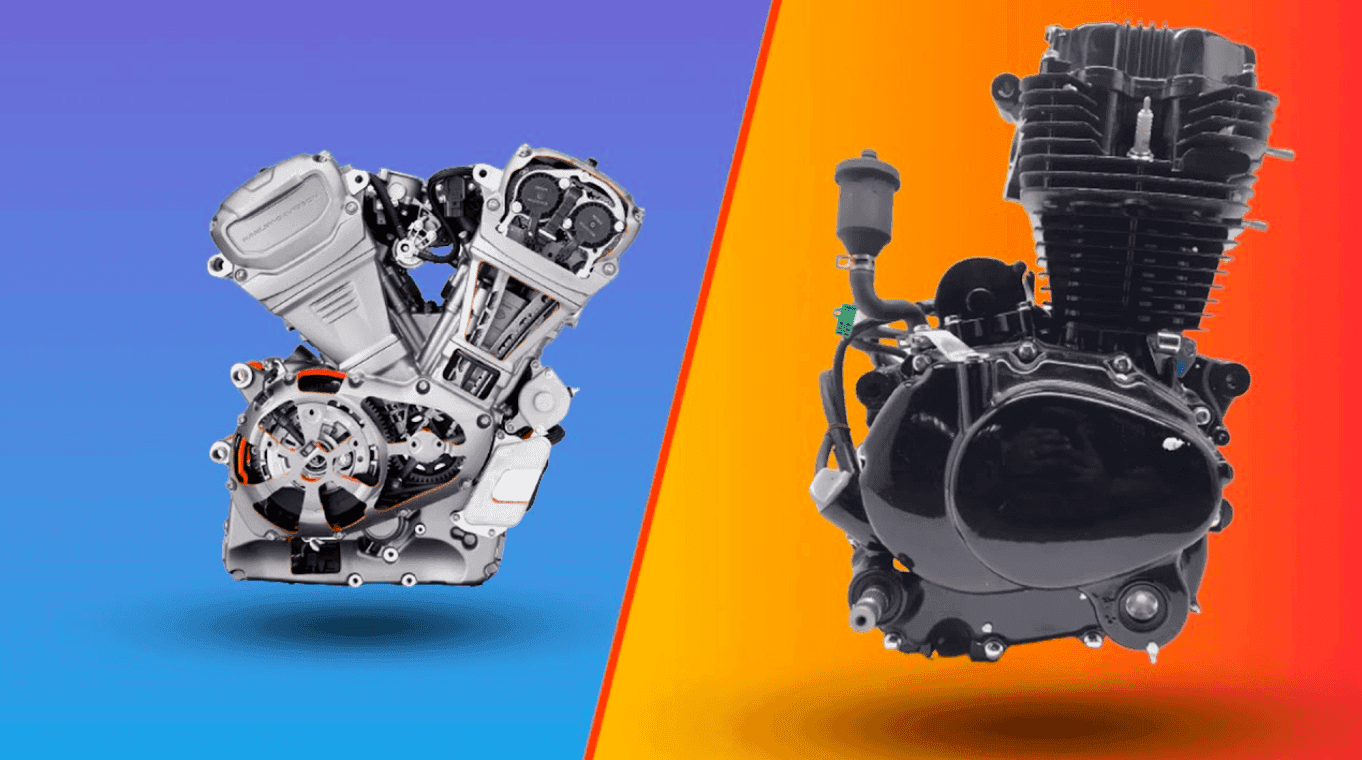
- V-Type Engine – Cylinders are arranged in a V-shape, allowing more power in a compact space.
- Opposed Cylinder (Boxer) Engine – Pistons lie horizontally, facing each other, offering balance and stability.
- W-Type Engine – Delivers high speed and power with multiple cylinder banks.
- Radial Engine – Cylinders are arranged radially around a central crankshaft, often used in aircraft.
From internal combustion engines to modern electric engines, the automotive industry has developed various engine types to meet performance, efficiency, and design needs. Understanding these classifications helps drivers, buyers, and enthusiasts choose the right vehicle. At MotorGuide, we believe knowing your engine type is the first step in proper vehicle care and performance.