What is Deep Discharging in an EV Battery?

If you drive an EV (electric vehicle), one of the most important things to understand is deep discharging. So, MotorGuide decided to explain what deep discharge is, why it is harmful, and what you can do to protect your EV battery.
What is Deep Discharge in EV Batteries?
Most modern EVs use lithium-ion batteries. “Deep discharge” happens when this battery is allowed to drop well below its recommended minimum State of Charge (SoC).
In normal day-to-day use, it is usually recommended to keep the battery between 20% and 80% charge. This range keeps the battery chemistry in a healthier zone and reduces long-term wear.
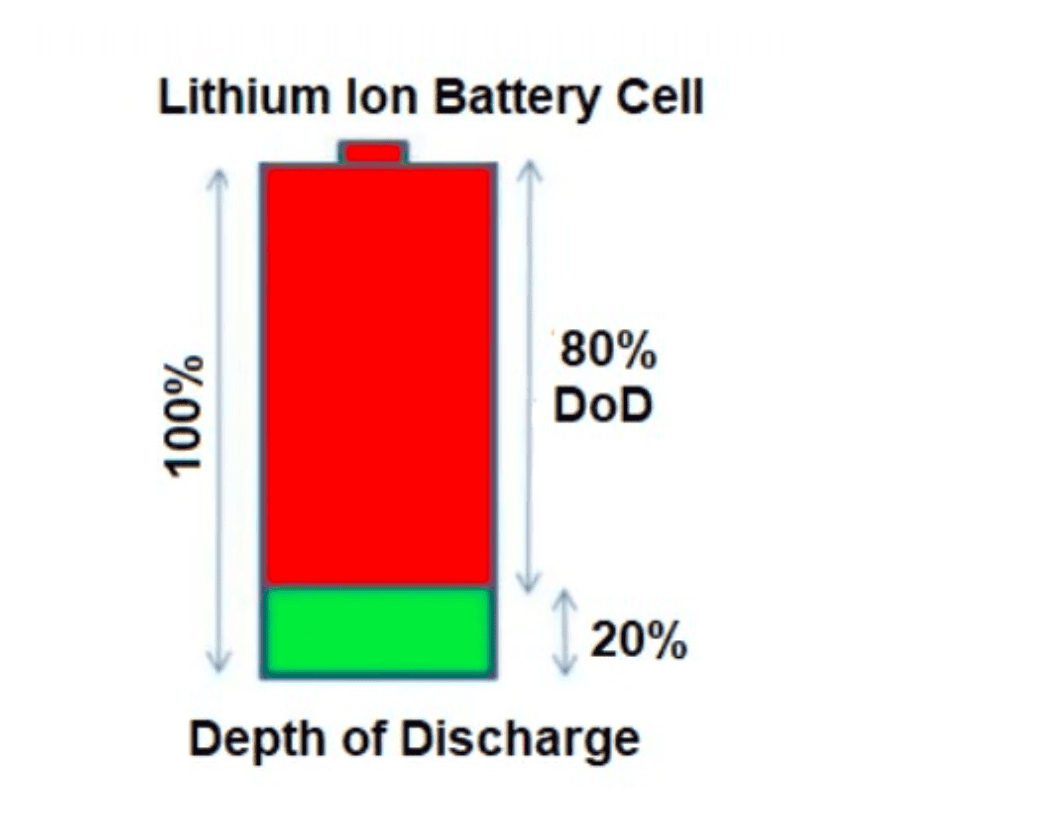
However, if the charge level drops repeatedly below 20% — especially down to 10% or lower — the battery is considered to be in a deep discharge state. Doing this often can seriously affect the battery’s health and lifespan.
Why Does Deep Discharge Damage the Battery?
Lithium-ion EV batteries are not designed to be fully drained on a regular basis. When they are, several types of damage can occur:
-
Internal chemical damage
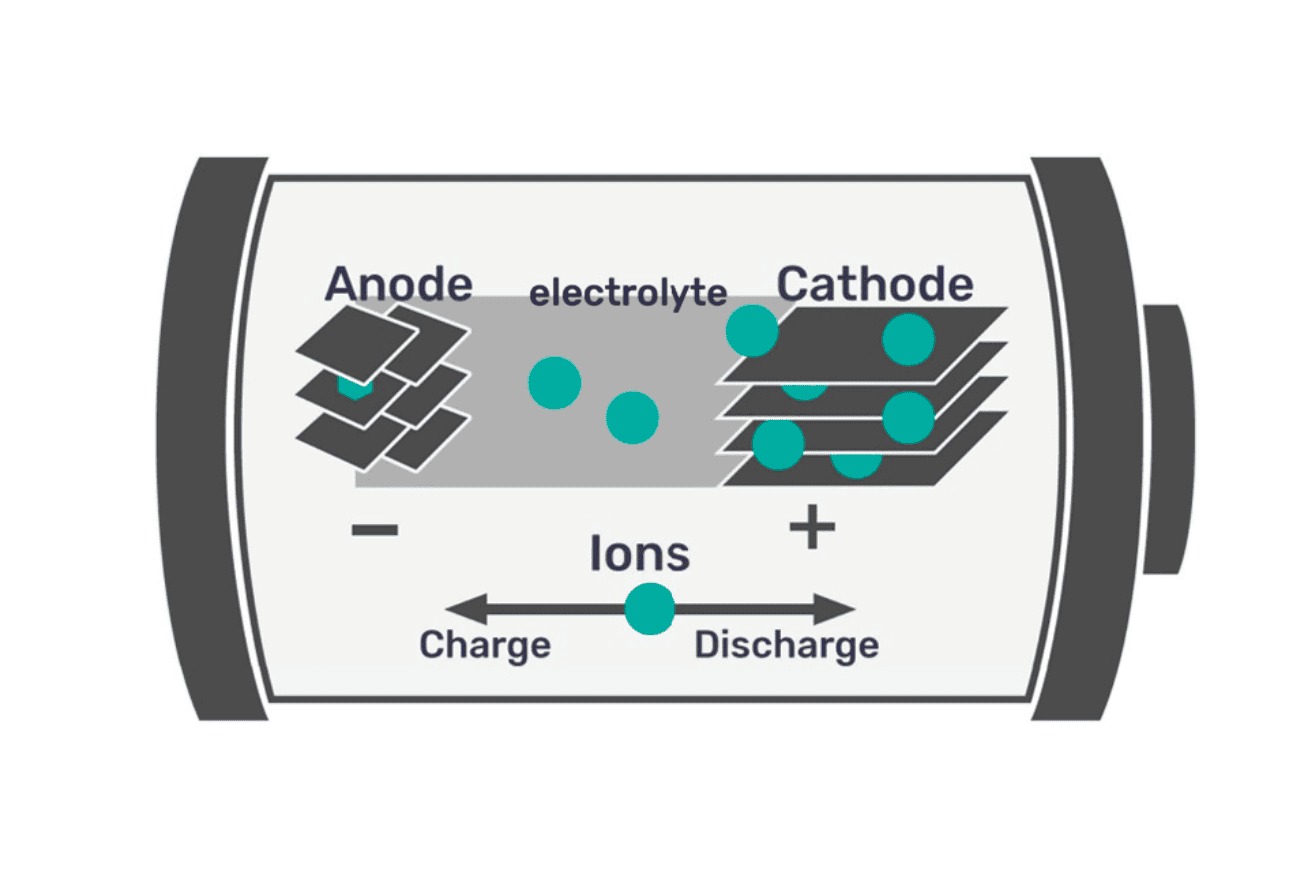
When the battery charge becomes very low, the chemical structure of the anode and cathode can change permanently. This reduces the battery’s usable capacity, meaning the car will not be able to travel as far on a full charge as it did when the battery was new. -
Lithium plating
After a deep discharge, when the battery is charged again, some lithium can deposit as solid metal on the anode (instead of moving as ions inside the electrolyte). This “lithium plating” blocks active material, lowers performance, and in extreme cases can increase the risk of internal short circuits and safety issues. -
Cell imbalance
An EV battery pack is made up of hundreds or thousands of small cells connected together. During a deep discharge, some cells can empty faster than others. Over time this creates an imbalance in the pack. The BMS then has to limit usable capacity to protect the weakest cells, which again reduces driving range and battery life.
How Do EVs Protect Themselves from Deep Discharge?
To reduce the risk of damage, EV manufacturers use an intelligent system called a Battery Management System (BMS). The BMS continuously monitors voltage, temperature, and State of Charge and takes action when the level becomes too low.
Typically, the BMS will:
- Warn the driver with low-battery alerts and messages well before the pack reaches a dangerous level (for example around 10–5% SoC).
- Limit power and performance to stretch the remaining range and protect the cells.
- At very low levels, completely shut down the vehicle to prevent the battery from going into a critical deep discharge zone.
How Can Drivers Protect Their EV Battery?
While the BMS offers protection, the driver’s daily habits make a big difference to battery life. A few simple practices can help:
- Avoid going below 20% regularly – Try to plan charging so that the battery does not sit for long periods under 20%. Occasional low dips are okay in emergencies, but it should not become a routine.
- Don’t fast charge from nearly empty all the time – Repeatedly fast charging from very low SoC puts extra stress on the cells. Whenever possible, start charging earlier.
- Don’t keep it at 100% every day – For daily use, it is usually better to charge up to around 80–90%. Save full 100% charges for long trips where you really need the maximum range.
- Avoid parking at very low charge – If the car is going to be parked for several days, try to leave it somewhere in the middle of the charge range (around 40–60%), not almost empty.
Key Takeaway
In simple terms, deep discharge means letting an EV battery drop below its safe minimum charge level. Doing this repeatedly can cause chemical damage, lithium plating, and cell imbalance, all of which reduce range and shorten the battery’s life.
If you keep your EV battery mostly within the 20%–80% range, avoid letting it sit at very low charge, and follow the warnings from the car’s BMS, you can significantly improve the long-term health and safety of your EV battery.