ඩීසල් එන්ජිමක කොටස්

Diesel engines - the underrated older brother
Unlike petrol engines using spark plugs to essentially create combustion ,diesel engines take advantage of high pressure within the combustion chamber to create energy. Common within heavy vehicles and machinery known for its longevity and continuous raw power. We're going to break down the diesel engine to its core and find out how this sparkles wizardry takes place.
Engine Block
Your engine block is the main structure that accounts and holds most of its components. A diesel engine block is cast or machined from aluminum blocks or steel as it is required to have a capability to withstand high pressure for longer periods of time.
Pistons
Pistons are your beating hearts in your engine. This is what compresses your air-fuel mixture to create combustion and transfer rotational motion to the crankshaft. Note that all components including the pistons of an engine block are manufactured in rugged materials or casting methods allowing them to withstand higher temperatures and pressures.
Crankshaft
Crankshaft is the axis in which the connecting rods of the pistons rotate along.The available pistons are connected to the crankshaft in a supplementing manner to make sure the crankshaft has peak rotational power in every degree of rotation.
Connecting rod
As mentioned earlier your connecting rods are the link between the piston heads and crankshaft in high speeds creating the RPMs
Sump
This is where all the used lubricating oil ends up after it has done its job before it goes back out through the lubrication process again.
Oil pump
Your oil pump works around the clock to make sure all your components are lubricated for optimal movement ranging from the piston rings around the wall to the connecting rod pins.
Cylinder head gasket
The cylinder head gasket sits in between the cylinder head and the engine block within the tight space to avoid any oil leaks and keep the seal clean.
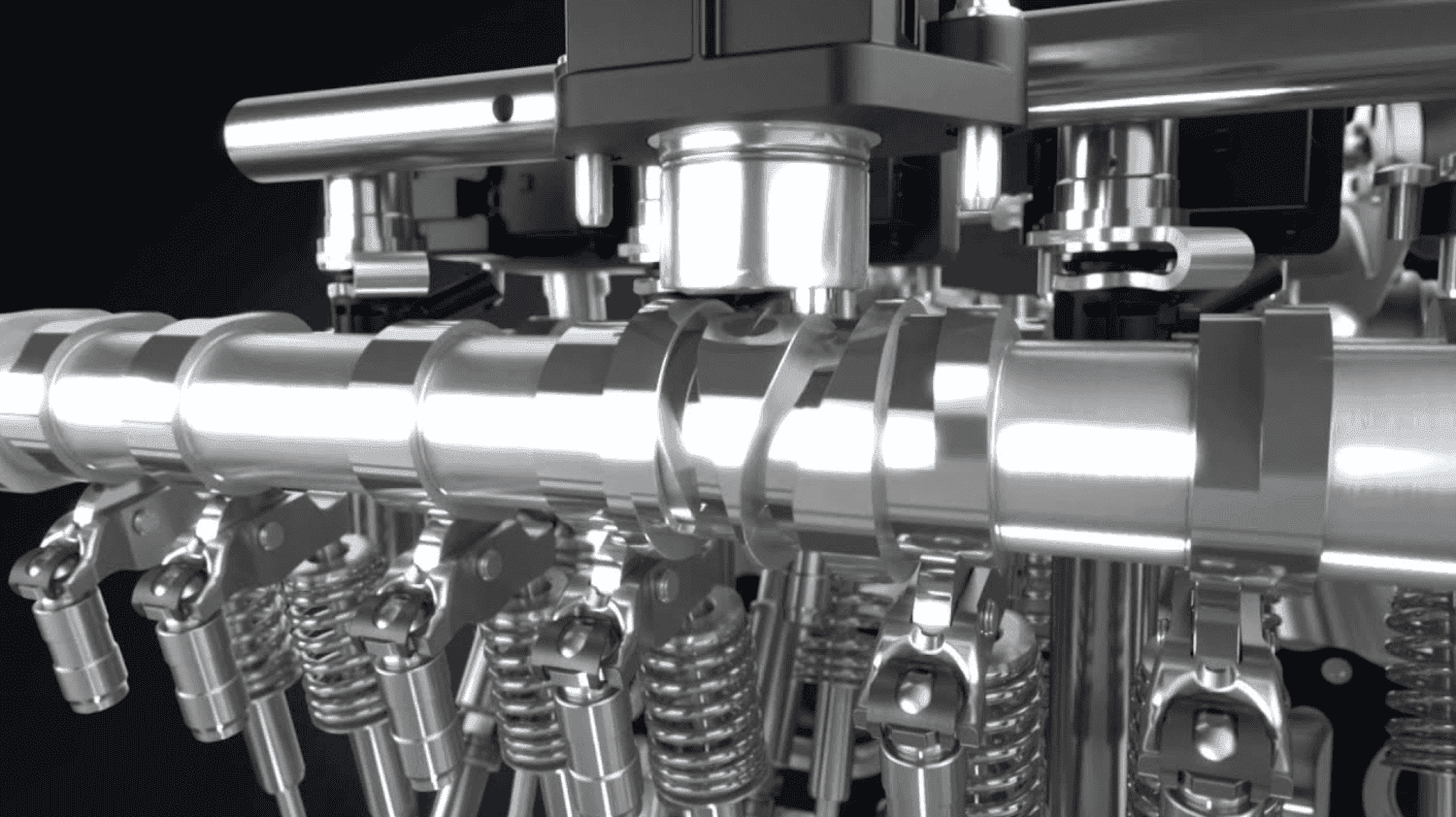
Valves
The inlet valves and the outlet valves are placed depending on the configuration to introduce air-fuel while expelling exhaust gasses respectively
Camshaft
The camshaft is a rotating shaft that sits above the engine block allowing air in and out of the combustion chamber at different timings for the different cylinders respectively.
Combustion Chamber
This is where the big bang place takes place to keep your vehicle in motion using air and fuel in a highly pressurized environment.
Bearings
Bearings are what keep things in motion smoothly without any mechanical interference.
Injection pump
It pressurizes the fuel to its limiting potential ready to be fed into the combustion chamber to create spontaneous combustion under extreme conditions.
Fuel injector
Using the pressurized fuel from the injection pump, it sprays it to the combustion chamber using small injector nozzles.
Now that you've heard of the components that goes into making your big and heavy diesel engine you would understand why this is typically heavier than petrol engines because of its use of high density materials to resist pressure. Using you knowledge on diesel engines now you can slip in and out of a conversation with a few diesel heads.